Google Ads are positioned directly within sight for the user, below the search bar, which is an attractive spot for advertisers. These spaces are auctioned off, whereby the highest bid is not crucial, but instead the results of Google’s internal review of the ad.

Google Ads: seconds-fast auctions for ad spaces
Keywords, CPCs, Quality Scores or Ad Rank are the main players of a Google Ad auction. But what do these terms even mean?
- Keywords are the important words the user types in during their Internet search. Ads associated with the matching keywords are shown as a result. They are also shown when one of the keywords is being searched for which the advertiser has provided.
- The cost per click, or CPC for short, tells you how high the price per click is. In other words, what the advertiser has to pay when the user clicks on one of their ads and is guided to the landing page. During the auction, advertisers state how high much they are willing to pay per click – the maximum CPC.
- The Quality Score for ads is calculated by Google in real time. The score is based on Google’s review of three characteristics: the expected clickthrough rate, the relevance of the ad, and users’ experience with the landing page. The quality is ranked between one and ten, whereby the rankings up to four is considered bad and the rankings from seven and up are good. This guarantees that the ads shown are professional, relevant and informative.
- To determine the Ad Rank, the ad’s Quality Score and the advertiser’s maximum CPC are offset with each other. This means all ads which match a certain search request are arranged fairly. The higher the Ad Rank, the better. But this is not to be confused with the ad position in regards to the concrete placement of the ad on the search results page.
The actual CPC is calculated based on the arrangement of the Ad Rank. This is extremely relevant, as the Google Ads auction is a so-called second-price auction. This means the advertisers who win do not pay the maximum CPC they bided, but just the sum to secure their ad position.
Step by step: how the auction works
A Google Ads auction is when a digital advertising space is auctioned off. This is how it works:
1. A user enters a search term in the Google search mask.
2. All ads matching this search request in terms of the keywords are shown.
3. The ads that cannot be shown are sorted out. The reason for this can be, for instance, that the rules have not been followed or due to the geographical location.
4. Of the remaining potential ads, just the one with the sufficiently high Ad Rank is shown. Here is where the Google parameters mentioned above come into play, the maximum CPC and the Quality Score.
An example: three advertisers would like to place their ad in connection with a keyword.
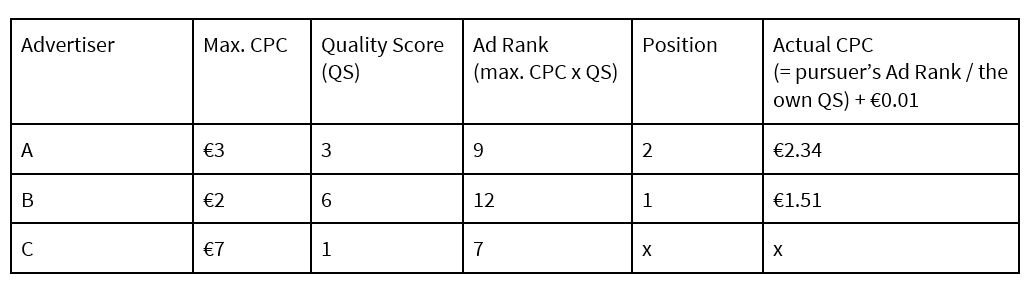
Note: In the last step, 0.01 euros are added to ensure the advertiser can keep their position against the pursuer.
In this example, the ad of advertiser B is in the first place below the search bar and a click costs them 1.51 euros. Advertiser A pays 2.34 euros per click and is in the second position. Advertiser C does not win the bid because their Quality Score is too low – despite their willingness to pay a comparable amount of money per click.
A tip: The more precise the keywords, the higher the probability to appear at the very top of the search results list and have to pay relatively little money for this.
